Configure a snap: using a content snap
When a robotics application is snapped, one might want to use it on multiple different robots.
Reusing the same snap means that we must be able to configure the snap to the specificity of a robot once installed on it.
For the rest of this guide, we will refer to the snap distributing the configuration as the configuration snap, and the one running the teleoperation application as the application snap.
We present in this guide the steps to distribute configurations with a separate, dedicated configuration snap and use it to distribute configuration files to another application snap.
Our application snap will get its configuration, not from the snapped package but from a configuration snap. This allows us to use the same snap on multiple devices with different configurations, as well as updating the configuration without having to update the application snap.
For this how-to-guide, we use the example ubuntu-robotics/snap_configuration.
The repository consists of the snapcraft.yaml file from which the snap is built, as well as a launcher script.
The repository contains a standard snap package providing the key_teleop application from the teleop_tool ROS 2 package. The goal here is to be able to configure the application using content-sharing, thus without having to update the application snap. The key_teleop node can be configured for its forward_rate, backward_rate and rotational_rate parameters. These are the parameters we will be configuring from the configuration snap.
Requirements
This how-to-guide is assuming that we are familiar with robotics snaps. Please refer to our tutorials to learn more about robotics snaps.
An up and running Ubuntu (minimum 20.04) with snapcraft installed is also required.
Configuration snap
In addition to an application snap containing our teleoperation, we will also distribute an independent configuration snap, only responsible for configuring our application. The configuration snap will simply contain the YAML file and make it available for the application snap via a content interface.
Create the configuration snap
The first step is to create a snap to distribute our configuration file.
Let’s create a new directory for the configuration snap:
mkdir snap
And then we can create the file snap/snapcraft.yaml with the following content:
name: my-configuration-snap
base: core22
version: '0.1'
summary: A snap to configure them all
description: |
This snap is sharing a configuration via content-sharing.
This way, my-ros2-teleop-test is getting configured.
grade: devel
confinement: strict
parts:
configuration:
plugin: dump
source: snap/local/
organize:
'*.yaml': etc/
The snap only contains one part, dumping local YAML files inside the snap. There is no application defined, since we don’t need one.
Define the configuration
Now let’s create the configuration file that our snap will be sharing.
First, we create a directory:
mkdir snap/local
We then create the file snap/local/up-to-date-config.yaml containing:
key_teleop:
ros__parameters:
forward_rate : 1.234 # our custom value
This configuration file only overwrites one value from the default one. This is the configuration that our application snap will use.
Declare the content slot
The configuration snap needs now to define the content interface. On the configuration snap side, we declare the slot part of the interface. Please refer to the online documentation for the explanation of slots and plugs.
We modify the snapcraft.yaml to declare the content slot:
grade: devel
confinement: strict
+slots:
+ configuration:
+ interface: content
+ source:
+ read:
+ - $SNAP/etc
The configuration is placed in $SNAP/etc here since etc/ is a standard directory for system configurations on Linux, but we could have used another directory such as $SNAP/teleop_config.
The configuration snap is now completed, we can build it and install it:
snapcraft
sudo snap install my-configuration_*.snap --dangerous
Our configuration snap is installed and ready to provide configurations!
Application snap
At the beginning of this guide, we introduced the ubuntu-robotics/snap_configuration. We start from this snap and modify it so that it uses our shared configuration.
First, we clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/ubuntu-robotics/snap_configuration.git
This repository already contains a snap package for the key_teleop package. There is a launcher script in snap/local/teleop_launcher.bash and the snap/snapcraft.yaml.
Declare the content plug
The configuration snap is exposing a content slot containing the configuration. To access this configuration, we must declare the content plug.
Let’s add the plug to the snapcraft.yaml:
grade: devel
confinement: strict
+plugs:
+ configuration:
+ interface: content
+ target: $SNAP/configuration
Additionally, we must declare that our application is using this plug:
command: bin/teleop_launcher.bash
-plugs: [network, network-bind]
+plugs: [network, network-bind, configuration]
Our application has now enough privilege to access the shared YAML file.
Before rebuilding our snap, we still need to actually use this file in our launcher.
Let’s see how to do that.
Use the content shared configuration
Even if we can access the shared configuration file, our launcher is still using the default configuration.
We will modify the launcher to make sure the shared configuration file is present and load it.
We modify the file snap/teleop_launcher.bash as follows:
#!/usr/bin/bash
+CONFIG_FILE_PATH="$SNAP/configuration/etc/up-to-date-config.yaml"
+if [[ -f $CONFIG_FILE_PATH ]]; then
-ros2 run key_teleop key_teleop --ros-args --params-file $CONFIG_FILE_PATH
+ ros2 run key_teleop key_teleop --ros-args --params-file $CONFIG_FILE_PATH
+else
+ echo "No configuration found!"
+ exit 1
+fi
As we can see, the content shared was entirely mounted in our target location.
Our application is now loading the YAML from our configuration snap!
Ensure content-interface connection between snaps
The content interface is auto-connect only when connecting two snaps from the same publisher, in other cases we really should verify the connection of the plug before launching our application.
Again, we modify our snap/teleop_launcher.yaml and prepend the following:
#!/usr/bin/bash
+if ! snapctl is-connected configuration; then
+ >&2 echo "Plug 'configuration' isn't connected, \
+ please run: snap connect ${SNAP_NAME}:configuration PROVIDER_SNAP:configuration"
+ exit 1
+fi
CONFIG_FILE_PATH="$SNAP/configuration/etc/up-to-date-config.yaml"
This way, the error message will be clear to the user in case the plug is not connected.
We are now ready to test, we can build and install the application snap:
snapcraft
sudo snap install my-ros2-teleop-test_*.snap --dangerous
We are now all set!
Test the snaps together
Both snaps are now installed. It’s time to make sure everything works fine.
We can verify the connections state of our application snap with:
$ snap connections my-ros2-teleop-test
Interface Plug Slot Notes
content my-ros2-teleop-test:configuration - -
network my-ros2-teleop-test:network :network -
network-bind my-ros2-teleop-test:network-bind :network-bind -
Since the content interface is not connected, we can manually connect it with the following command:
sudo snap connect my-ros2-teleop-test:configuration my-configuration-snap:configuration
We can now launch the application with:
my-ros2-teleop-test
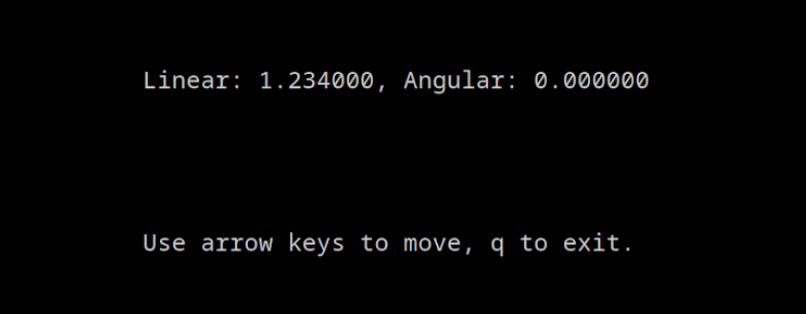
By pressing the “up” arrow, we can observe that the value from our configuration snap (1.234) is used!
With the application snap properly using the YAML provided by our configuration snap, we can now update the configuration easily and independently of the application snap.
We can use the same application snap on multiple robots and provide a different configuration snap to different robots. We can also ship many configuration files in the configurations snap serving multiple application snaps!
We can find the complete example of this how-to-guide (application and configuration snap) on the branch howto/content_sharing_configuration_snap of the repository.